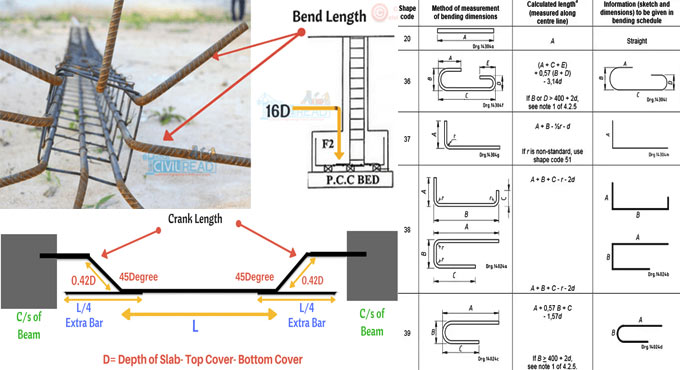
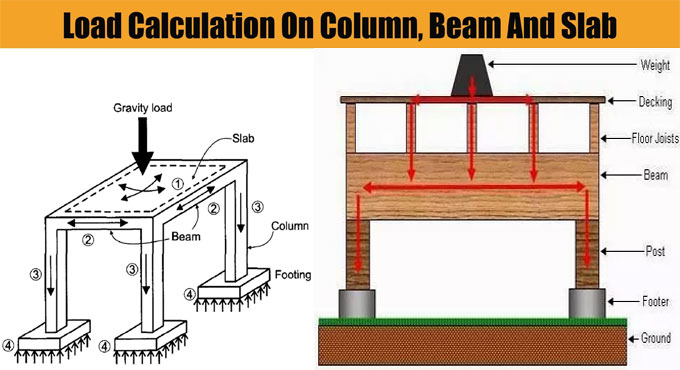
The finalized inspection of concrete formwork should be examined prior to set the reinforcement bars in exact location. By implementing perfect form work, honey combing, blow holes, grout less or discoloration of concrete can be circumvented and consequently the finished surface of concrete becomes superior.
Prior to commencement of concreting work, shuttering surface should be fully cleansed and does not contain any defect/deposits in order to provide rightly straight smooth concrete surface. Shuttering surface does not contain any damage and unnecessary roughness to its surface.
While building concrete form work, the following should be examined properly.
1. Any member to be retained in position once the general dismantling is completed, should be labeled perfectly.
2. The applicable materials should be thoroughly examined in order that no incorrect items/rejects are utilized.
3. When excavations exist nearby reformatory and strengthening action should be undertaken to impact the safety of form work.
4. The quality of bearing soil should be strong and it should be arranged properly and the sole plates should bear well on the ground. Sole plates should be perfectly placed on their bearing pads or sleepers. The bearing plates of steel props should not be deformed. There should be adequate bearing areas for the steel sections on the bearing members.
5. There should be proper safety provisions to get rid of impact of traffic, scour caused by water and accidental impacts.
6. To maintain proper strength and durability of form work at intermediate stage, bracing, struts and ties should be provided together with the advancement of form work. Avoid ‘Tilting and overturning of steel sections.
7. While applying customizable steel props, no damage and evident bents should be observed; steel pins should be arranged, restricted latterly near each end.
8. Screw adjustments of adaptable props should not be over extended.